- Cognitive biases happen because of six reasons:
- Top 20 Cognitive Biases Every Digital Marketer Should Know
- FAQs
- 1. This information leads to the following questions: What are the Cognitive biases in digital marketing?
- 2. How would cognitive biases be helpful to enhance digital marketing?
- 3. What role does the Anchoring Bias play within the formation of price control mechanisms?
- 4. What is Social Proof in digital marketing?
- 5. Is it possible that cognitive biases be destructive in digital marketing?
- 6. In what way does the Scarcity Bias influence its sale?
- 7. What does the IKEA Effect mean to product customization?
- 8. How Digital Marketing Agencies can use the Decoy Effect?
- 9. It is worth knowing what the Halo Effect does to the overall evaluation of the brand.
As humans, we greatly pride ourselves in sophistication and intelligence and as such, we believe we are the most logical creatures on the face of the earth. People’s decisions are not perhaps as rational as they want to think they are. Our brain, however smart it may be that the smartest computer in the world over has several prejudices that prevent us from solving things logically. Most of the time, the perception arising from previous experiences, emotions, and feelings guides the decisions that we make that may not necessarily be perfect.
Cognitive biases happen because of six reasons:
Memory: Our memory is a tricky source of information. Sometimes we recall an event that has never happened
Social: Our social upbringing may contribute to favoring the group’s decision
Learning: building on concepts acquired at an early age(Need more explanation)
Belief: Clinging on to beliefs that one feels are the gospel truth always plays a vital role in decision-making
Money: One’s perspective about money highly influences their decision making
Politics: Political views define the decisions based on affiliations to gain a political edge and can shape the process
These are known as cognitive biases which refer to the error that is made when in the act of processing information and arriving at a decision. In most cases, two or more of the above factors influence every cognitive bias that we come across.
Top 20 Cognitive Biases Every Digital Marketer Should Know
1. Anchoring Bias
Anchoring Bias refers to a tendency that people habitually have to use an initial reference point or a piece of data (known as the ‘anchor’) while concluding. In digital marketing, this can be used by setting an initial high price for a product and then providing discounts; this makes the sale price look more appealing as compared to the set high price.
Example: Flipkart
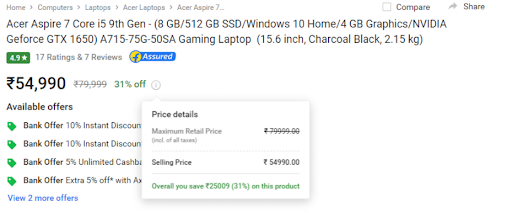
In this example, if anyone looking to buy a laptop sees this much amount of discount, there are many chances he may grab this offer.
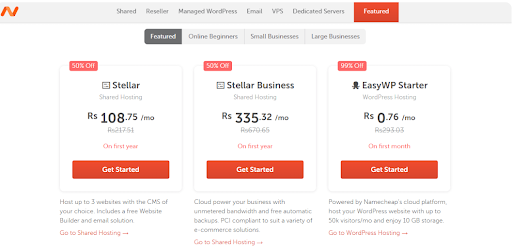
In B2C also this cognitive bias is used extensively, take a look at these pricing tables available. This clearly shows we are going to save a lot of money.
The anchoring effect is a critical part of NEGOTIATION.
2. Social Proof
Social Proof is the reliance of the masses on other people to follow specific behaviors, especially when in a dilemma. This is a good approach in the use of cognitive bias marketing since perceived behavioral cues are usually used by consumers.
Example: Using customer feedback and recommendations or informing the customers the number of customers, who have bought the product, to compel the new customers to do so.
3. Scarcity Bias
Scarcity Bias is the effect where an individual considers a particular product valuable because it is scarce. Digital marketers can particularly exploit this bias as they can establish a time-bound offer on their products or services.
Example: Using an emphasis such as “Only 3 left in stock”, “Limited time offer” and such to persuade people to buy the products.
4. Bandwagon Effect
The Bandwagon Effect is also known as conformity theory where people change their attitude or behavior based on others in the same group.. This bias can be utilized to generate demand for a product or service as a way of displaying to customers that more people use it.
Example: Amazon -reviews
One more natural tendency is to read the reviews before selecting items that one would like to purchase. This is well-used by Amazon.
5. Loss Aversion
Loss aversion can be defined as people’s inclination towards risks regarding loss instead of attaining gains of equal value. Digital marketers can use it by highlighting what customers are likely to lose in the event they do not take any action.
Example: Amazon
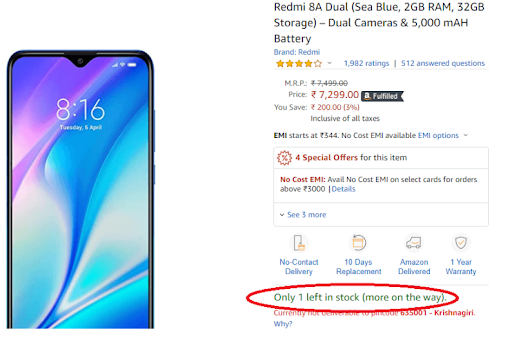
Fear of Missing out(FOMO) is always active in the human brain. This bias has been used from as early as the prehistoric era and yet it is one of the most effective strategies in use
6. Confirmation Bias
Confirmation Bias is prejudice in which a person gathers facts that support their opinions only. The Information interfaces of Web 2.0 enable DMAs to fine-tune content to be in line with the direction of opinion or preference that already exists in the target audience.
Example: Creating an ad appeal that suits the customer, his/ her preexisting mentality, or propensity to purchase such products as green products for green consumers.
7. Authority Bias
The presence of the Authority Bias means that accuracy is attributed to the opinion of an authority. This can be applied in social media marketing by linking a product or a service with some key opinion leaders.
Example: Such as using endorsements from expert persons or celebrities to support a product.
8. Endowment Effect
The Endowment Effect is a psychological bias wherein people overprice things simply because they own them. This could be taken advantage of by providing a ‘free trial’, ‘free samples’, etc, as people are inclined to buy something that they already feel they possess.
Example: Amazon offers this promo to try out their Over The Theater services. This is understandable since if people get accustomed to the convenience at which Prime Video provides a movie, then they will continue doing so in the future.
9. Halo Effect
The Halo Effect can be defined as an overall assessment of all the traits of a person based on a positive interpretation of one trait. In cognitive bias marketing, this can be used by relying on a single aspect of a particular product.
Example: Using the fact that a particular product has an award-winning design to change people’s perception of the quality of that product.
10. Framing Effect
The Framing effect results from people’s behavior changing based on the way information is presented. This makes it possible for digital marketers to guide the decisions being made by framing the messages appropriately.
Example: For instance, if there is a negative attribute of a product masked in wordplay that describes its usefulness, then the product is likely to do well.
Example of Execution: Netflix: Sign up Page
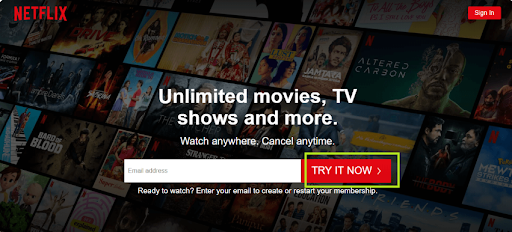
The signup page is perfectly designed at Netflix with a single visible CTA- TRY IT NOW.
Furthermore, they have only requested for email address as one of the details which would lessen a person’s workload.
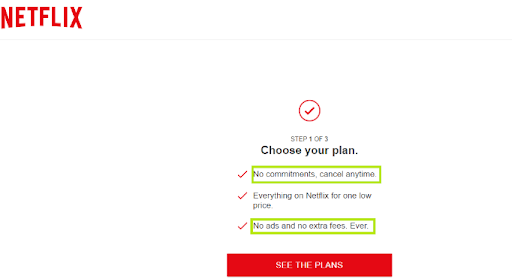
It continues on the next page, where all the benefits of it are listed, as well as fewer risk factors.
Selecting the plan is also well-framed Netflix shows that BASIC is the default option by making the column bold.
Last but not least, this place is also showing the aspect of ‘getting instant pleasure’ in their ads.
This is how the framing effect can bias our customers in numerous ways, it makes them relaxed in our hands and very little effort is expected from their end.
11. Paradox of Choice
Generally, the state of having many choices is regarded as a positive one. Unfortunately, with greater options, decision-making results in overthinking or ending up not deciding at all.
Companies may decide options in a way that there are cases of paradox of choice, whereby the existence of more options forces customers to seek the services of another firm or become fallbacks.

This is due to what is referred to as the ‘paradox of choice’ where choice, as described in a book by Barry Schwartz is a very difficult thing. In some industries, it is always important to note that options can also deter the customer by making him/her confused when making a purchasing decision.
It may also be noted that “learning to choose is hard and learning to choose well is even harder and it is very, very hard when the options to choose from are limitless.”
-Barry Schwartz, The Paradox of Choice: A Musical Interlude and Image. Figure adapted from ‘Exploded: More is Less = Less’, Timothy Noone Why More Is Less
12. Availability Heuristic
Anyone has ever realized that sometimes logic is ignored for the benefit of the appeals to emotions?
If rationality has been trumped by recent events that create a highly perceived utility then it would be safe to assume the availability heuristic has occurred.
From this bias, consumers are said to have irrational behaviors when selecting items, and later on, they make rational arguments in a bid to justify the chosen item.
With regards to marketing, once it gets established in the minds of the consumers that a certain product has a ‘need factor,’ consumers will purchase the product and then justify the necessity of the purchase afterward.
Example in Execution: Coca-Cola
Everyone has probably taken a Coke at some point in their lifetime but how many have contemplated the instrumental value of having a Coke?
13. In-Group Bias
In-group bias is general favoritism toward members of a particular group in comparison to other groups. This bias can be encouraged by Digital marketers by ensuring that the brand has a sense of community.
Example: Design thinking for offering special privileges to the customers to make them feel valued and important or to form a loyalty program for consumers.
14. Sunk Cost Fallacy
The Sunk Cost, which is a type of cognitive bias refers to a scenario whereby an individual persists in a particular endeavor due to the amount of money, time, energy, etc.; he or she has already spent on the activity despite the actual results. This bias can be addressed by using information about consumers’ efforts as a valuable tool to determine the value of a product or a service.
Example: Recalling the subscribers to the services and products that they already subscribed to so that they can renew their subscription.
15. Overconfidence Bias
Overconfidence Bias – this is the Bias where people tend to assume more than they should or know more than they do. This bias can be leveraged by digital marketers by providing challenges or quizzes that make the consumer feel right about themself or make them feel that they are right.
Example: Creating an online quiz for users to complete that makes them feel informed, then providing a product that relates to their quiz results.
16. Herd Mentality
Social loaf is the unresponsiveness or the attitude most people take when in a group or around other people. Digital Marketing Agencies questions will be asked if a customer returns a product to helps in easing the perceived risk barrier thus encouraging customers to pick their preferred products.
18. IKEA Effect
The IKEA Effect is defined as a tendency of consumers to assign higher value products to which they had a part in assembling. Such a bias can be taken advantage of by providing choices for customization
19. Decoy Effect
The Decoy Effect is applied when a consumer shifts his or her preference between two related products upon the introduction of a less preferred product. This can be adopted by digital marketers to guide customers towards better-margin products.
Example: Developing a pricing scale that has numbers with one of the scales having better features meant to make the top scale seem the best offer.
20. Primacy Effect
The Primacy Effect is a form of the CET that entails having better memories of the first data learned than the data learned later. This can be done by Digital Marketing Agencies by prioritizing their information while coming up with content.
Example: To ensure that the audience gets the most out of the message being passed by the landing page, the key benefits of a certain product are normally presented at the initial stage.
Conclusion
If one is to enhance the impact of marketing efforts within the context of a Digital Marketing Agency or a Digital Marketer, then it is important to comprehend and utilize cognitive biases. Such biases offer information about consumer behavior, thereby helping marketers to develop more effective messages, and appealing content and thereby better outcomes. Introducing these factors of cognitive biases into your digital marketing campaigns will give you a clearer understanding of how to effectively get your audiences’ attention to ultimately allow for your goals to be met.
FAQs
1. This information leads to the following questions: What are the Cognitive biases in digital marketing?
Cognitive biases on the other hand are thus systematic patterns of deviation from rational behavior that impact the consumer. It means that these biases are available for digital marketers to exploit and make their campaigns more effective.
2. How would cognitive biases be helpful to enhance digital marketing?
Knowledge of cognitive biases helps digital marketers make more persuasive content, enhance consumer engagement, and increase conversions since marketing strategies adhere to consumers’ inherent ways of thinking.
3. What role does the Anchoring Bias play within the formation of price control mechanisms?
The effect of Anchoring Bias is that consumers tend to think that certain discounts and deals are good because an initial high-priced tag influences their usual perception.
4. What is Social Proof in digital marketing?
Social Proof uses the Bandwagon Effect by redirecting new users to the fact that many others have made a purchase or taken a certain action.
5. Is it possible that cognitive biases be destructive in digital marketing?
Indeed, if applied wrongly or if the consumers do not know they are being appealed to based on their cognitive biases, it may cause distrust among the consumers towards the brand.
6. In what way does the Scarcity Bias influence its sale?
Scarcity Bias is another approach that focuses on the concept of scarcity and tells the consumers that the product is limited and they should buy it immediately.
7. What does the IKEA Effect mean to product customization?
The IKEA effect hypothesizes that people put much importance on the things they build themselves and as such, customization is a potent weapon in the arsenal of perceived value.
8. How Digital Marketing Agencies can use the Decoy Effect?
The Decoy Effect can be applied to agencies, where there is introduced a third option which is less attractive compared to the favorite one.
9. It is worth knowing what the Halo Effect does to the overall evaluation of the brand.
The Halo Effect means that it is possible to change the general picture of the brand for the better by focusing, for example, on a positive aspect of the company, this bias proves how many people are interacting with a particular brand or item.
Also Read: Top 20 Performance Marketing Agencies in India 2024
